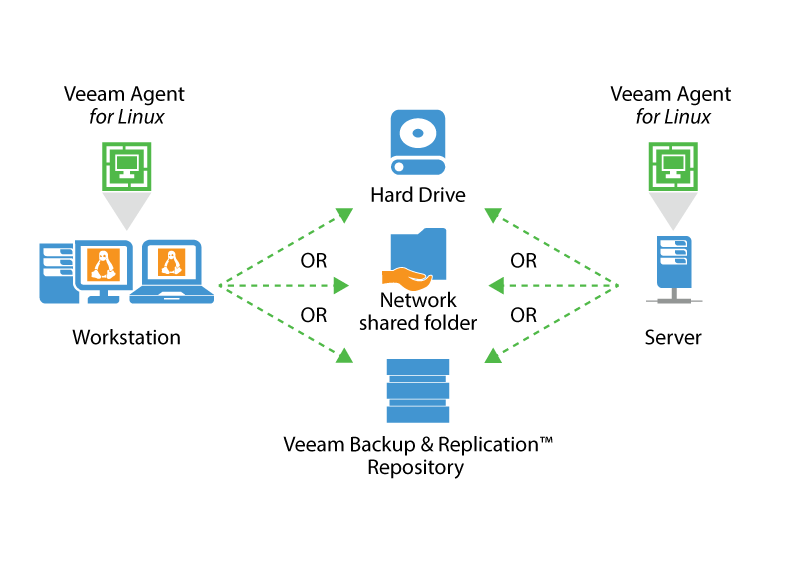
Để monitor Dynamic Memory của VM trên Hyper-V có thể sử dụng tool Performanca Monitor của MS. Tool này cung cấp nhiều thông tin bổ ích như Guest Visible Physical Memory, Physical Memory, Current Pressure.
Quick Monior: Bạn nhấn Ctl + N để thêm Hyper-V Dynamic Memmory VM. Chọn VM cần monitor -> click Add. Sau đó click OK.
Continue reading “Monitor Hyper-V Dynamic Memory trên Windows 2016”